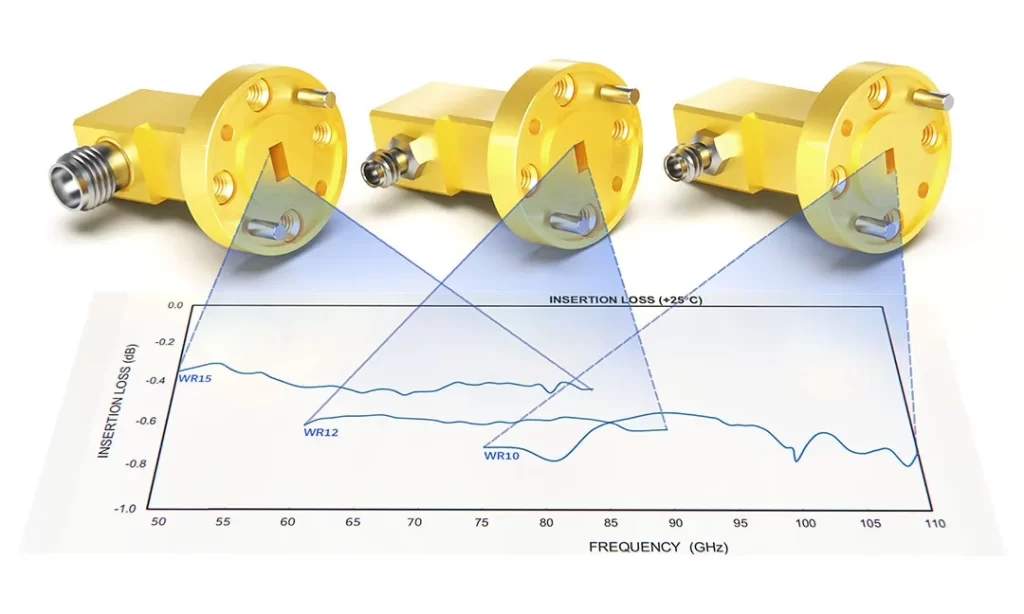
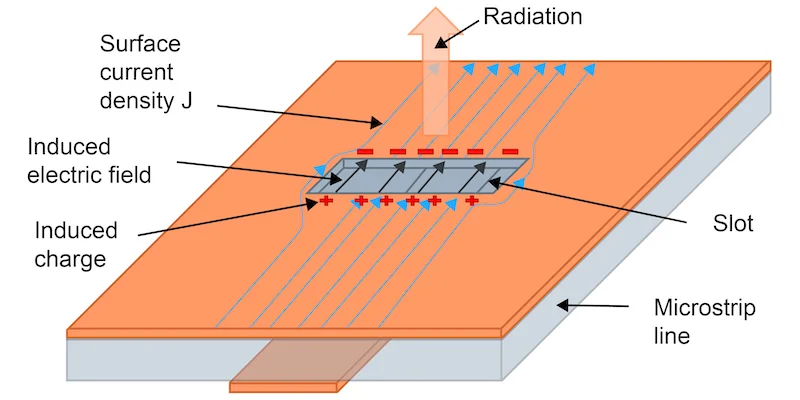
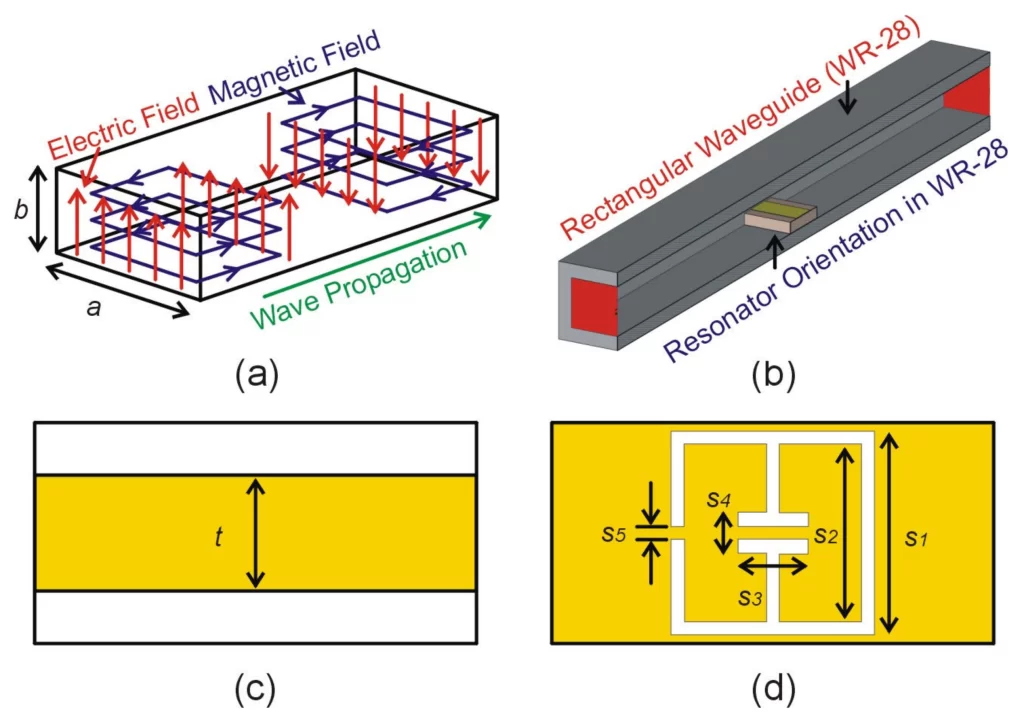
What is the role of waveguide duplexers in communication systems
Waveguide duplexers are crucial for allowing a single antenna to simultaneously transmit and receive signals, often operating in frequency ranges like 3.5-4.2 GHz. They use internal filters to provide high isolation, typically over 30 dB, preventing powerful transmitted signals from overwhelming sensitive receivers, which is vital in radar and cellular systems. What is a Waveguide […]
What is the role of waveguide duplexers in communication systems Read More »