Why Use Waveguide Components in Millimeter Wave Systems
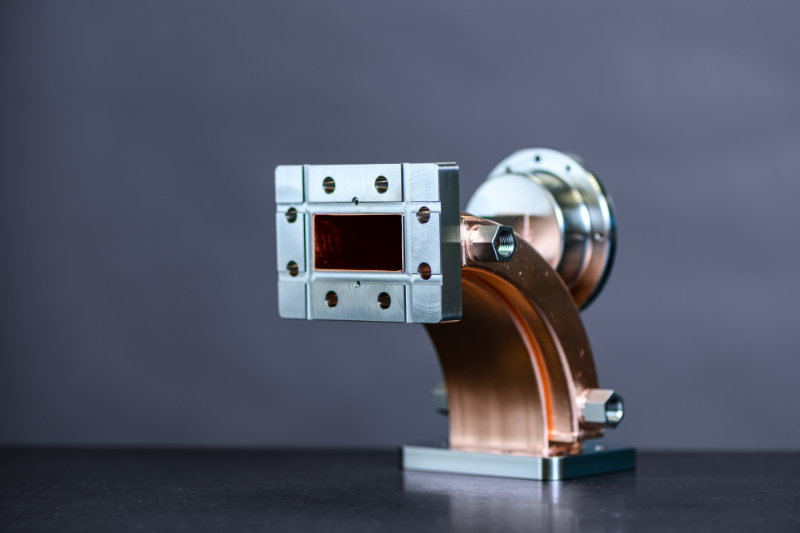
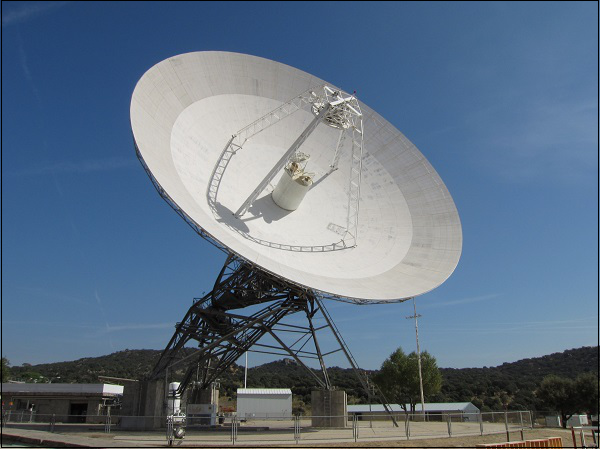
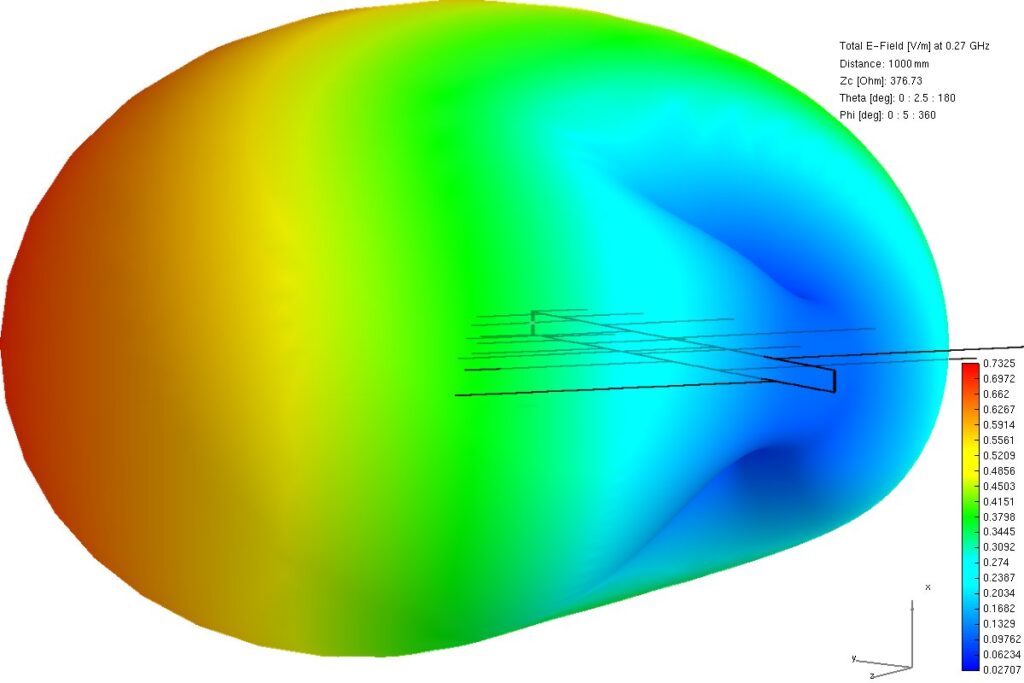
Waveguides dominate mm-wave (26-100GHz) systems: their low loss (<0.1dB/m at 60GHz for rectangular types) beats microstrip, while high power handling (10s of W) suits radar/5G; tight field confinement ensures stable, high-fidelity signal transmission critical for long-reach links. Extremely Low Transmission Loss When the frequency jumps from the familiar 5GHz Wi-Fi to millimeter-wave bands like 28GHz, […]
Why Use Waveguide Components in Millimeter Wave Systems Read More »