How does electromagnetic waveguide theory apply to antenna design
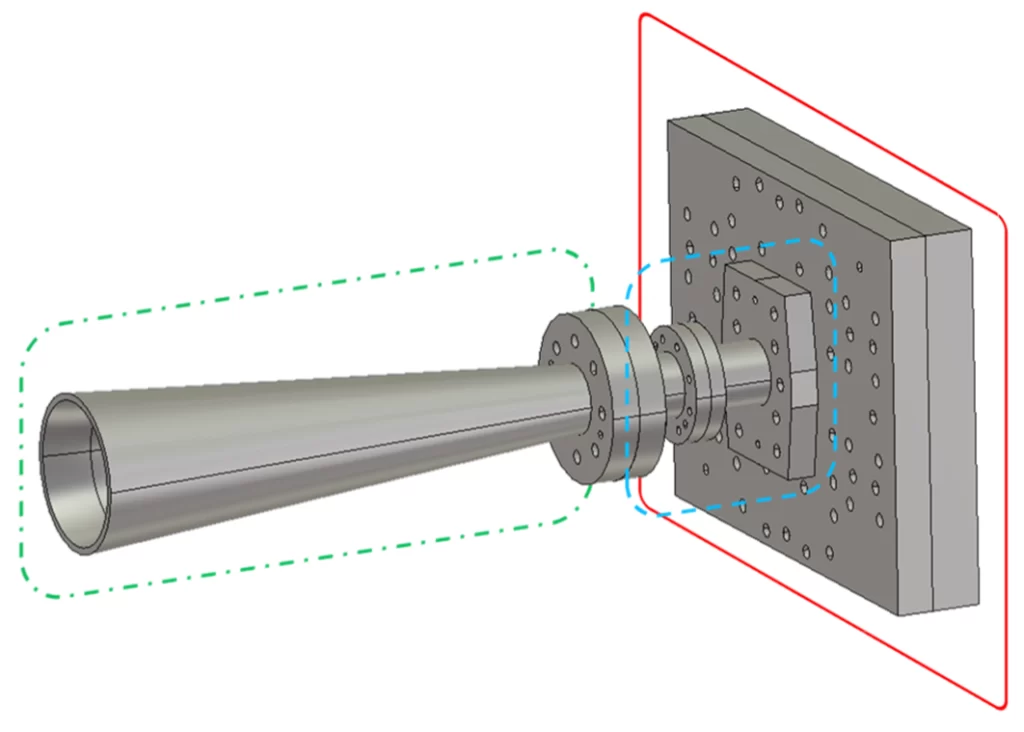
Electromagnetic waveguide theory underpins antenna design by shaping radiation patterns and optimizing feed structures. For example, rectangular waveguides—common in horn antennas—operate at 10 GHz using a 22.86mm height (WR-90 standard), supporting TE10 mode with a cutoff frequency of ~6.56 GHz. Impedance matching via waveguide-to-microstrip transitions reduces VSWR to <1.5, enhancing power transfer efficiency by 20-30% […]
How does electromagnetic waveguide theory apply to antenna design Read More »