What is the difference between directional coupler and splitter
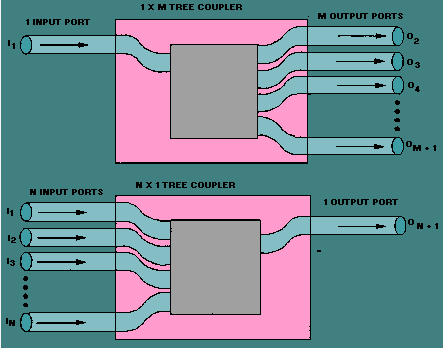
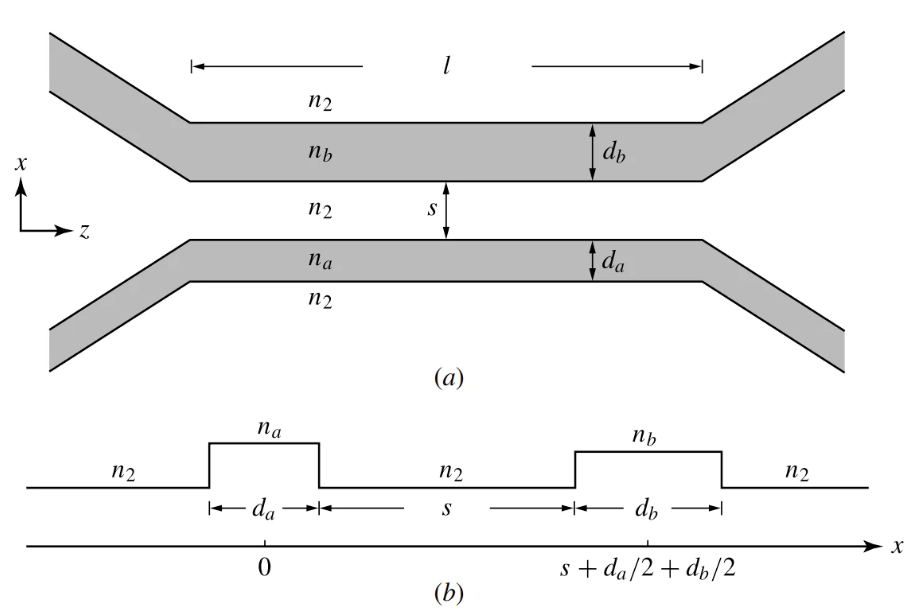
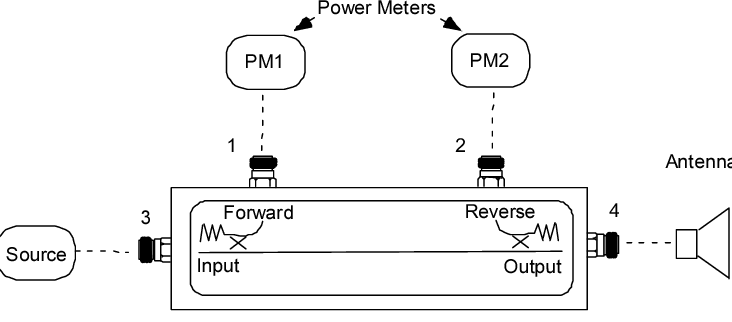
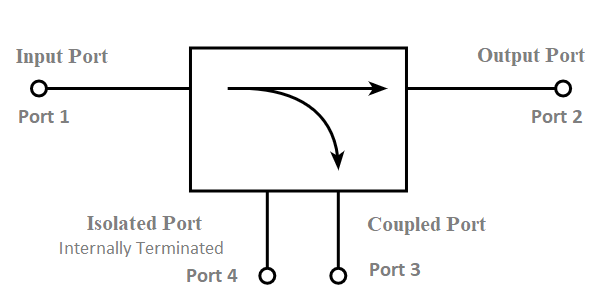
A directional coupler samples a small portion (e.g., -10dB to -30dB) of signal flow in one direction (forward/reflected) for measurement, while a splitter divides power equally (e.g., 3dB loss per port in a 2-way splitter) across all outputs. Couplers maintain isolation (20–30dB), whereas splitters balance impedance (75Ω/50Ω). Use couplers for RF analysis, splitters for signal […]
What is the difference between directional coupler and splitter Read More »