What are the 4 best waveguide antenna kits for beginners
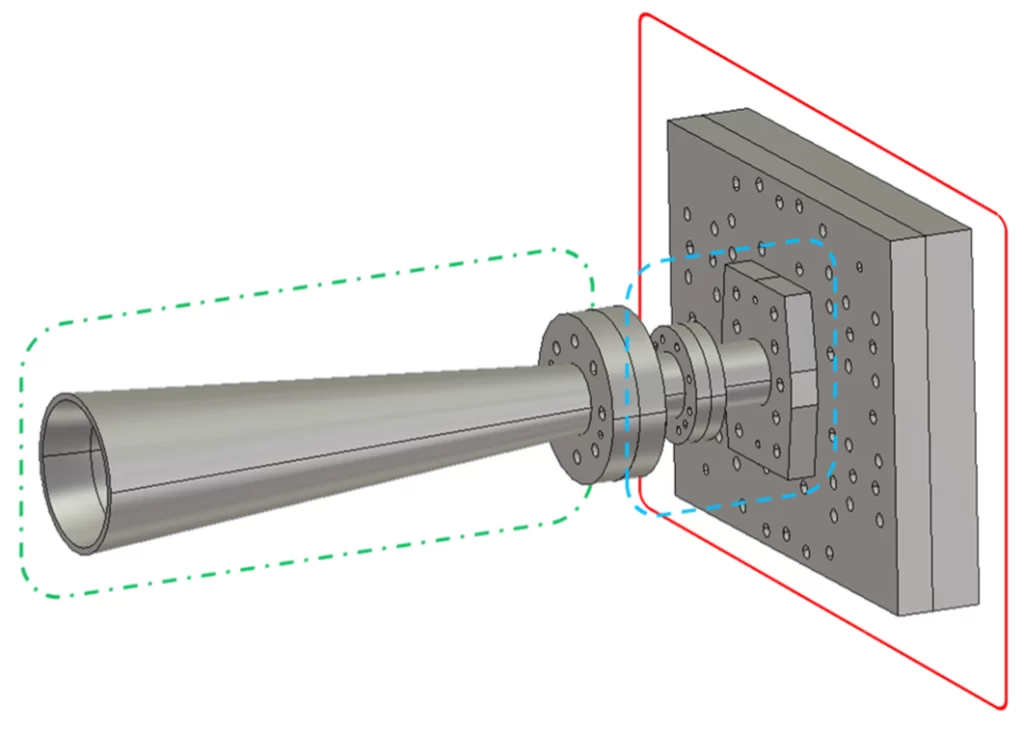
For beginners, the 2.4GHz WR-430 waveguide kit is highly recommended for its manageable size and common frequency band. The N1200 kit for 10 GHz is another great option, often used in satellite TV experiments. Look for kits that include pre-cut parts, like those from KM5DIY on eBay, which help avoid precision cutting. Lastly, consider a […]
What are the 4 best waveguide antenna kits for beginners Read More »